RuiPath Pathology Model Open-Source Launch: A Leap Forward for China's Medical AI Ecosystem
On the afternoon of June 30, 2025, the "RuiJin Hospital RuiPath Pathology Model Open-Source and Achievements Conference" was held in Shanghai. Hosted by Ruijin Hospital, affiliated with Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine (hereinafter referred to as "Ruijin Hospital") and co-organized by Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd., the event marked the global open-sourcing of the core architecture of RuiPath, a groundbreaking pathology large model. This milestone signifies China's medical AI has achieved a transformative leap from technological breakthroughs to ecological sharing.
About the RuiPath Pathology Model
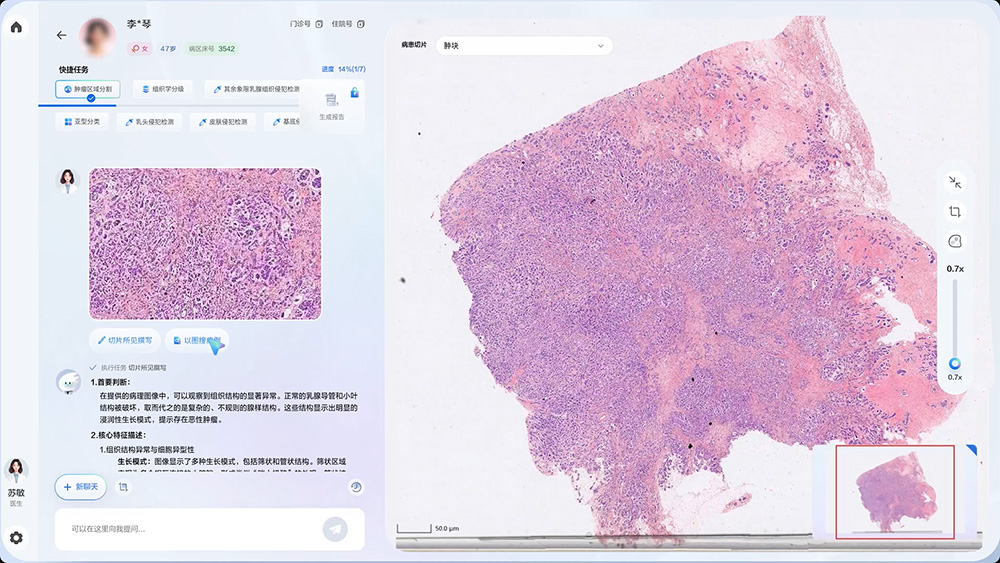
Developed by Ruijin Hospital with support from Huawei, RuiPath is a clinical-grade multimodal pathology large model. It integrates capabilities such as pan-cancer visual feature extraction, cross-layer alignment of visual-language representations, and training mechanisms for long-sequence deep reasoning models. Designed for full-process clinical pathological auxiliary diagnosis, it currently covers 19 common cancer types, accounting for 90% of annual cancer incidences in China, and supports over 100 auxiliary diagnostic tasks.
In his speech, Academician Ning Guang, President of Ruijin Hospital and member of the Chinese Academy of Engineering, noted that pathology large models face two critical challenges in transitioning from technological release to clinical application: insufficient clinical coverage and limited accessibility. To address these, Ruijin Hospital and Huawei achieved a "dual open-source" breakthrough: first, open-sourcing a dataset of 700 digital pathology slides for evaluation; second, open-sourcing the algorithm model. These efforts aim to build an industry-academia-research collaboration ecosystem. He expressed hope that the open-sourcing and achievement-sharing will gather diverse forces to refine the model, rigorously validate clinical safety, and help develop a vertical medical AI ecosystem.
The severe challenges facing the industry today include a huge shortage and uneven distribution of pathologists, as well as low consistency in primary diagnosis at the grassroots level. Digital intelligent pathology offers a solution, and the open-source RuiPath model provides an effective answer to these issues.
Key Breakthroughs of RuiPath
· Data: Established a leading national-level repository of millions of high-quality pathology slides covering common cancers and rare diseases.
· Algorithms: Adopted the "intelligent learning system" (PanVL-T1 technology). Among 12 mainstream public datasets and 14 auxiliary diagnostic tasks, 7 tasks achieved world-class performance in AUC, ACC, and F1 score, comparable to top global models.
· Computing Power: Successfully trained millions of slides using 16 domestic chips for the first time.
· Storage: Reduced storage space by up to 45% through compression technology, and shortened training cycles by 30% via storage-computation synergy.
At the conference, guests witnessed the official open-sourcing of RuiPath's visual foundation model. Built on Ruijin Hospital's millions of high-quality digital pathology slides and developed using Huawei's full-process AI toolchain for annotation, training, and fine-tuning, the model has reached industry-leading levels with clinical validation capabilities. Notably, the open-sourcing includes test datasets covering 7 common cancers—lung, colorectal, thyroid, gastric, breast, prostate, and pancreatic cancer—to promote inclusive development of medical AI in pathology.
WINMEDIC expressed pride in contributing to RuiPath's development through high-quality digital pathology solutions. During image acquisition, WINMEDIC provided the Win-300-Pro brightfield-fluorescence integrated digital slide scanner and supporting software. The high-resolution, high-fidelity panoramic digital slides ensured smooth AI annotation, training, and fine-tuning, boosting confidence in operators and data results. With a single loading capacity of 300 slides and fully automated high-speed scanning, a large number of precious samples were quickly imaged, accelerating model development and release.
Since the initial release of RuiPath in February 2025, trained on single-center data from Ruijin Hospital, the model has undergone continuous optimization, evaluation, and application development, with steadily improving performance. At the conference, Ruijin Hospital joined hands with 12 domestic and international medical institutions to launch the RuiPath Pathology Large Model Global Multicenter Plan, aiming to share research achievements and drive collaborative iteration.
Professor Wang Chaofu, Director of the Pathology Department at Ruijin Hospital, outlined three core goals of the initiative:
· Enhance Accessibility: Promote high-quality pathological resources and RuiPath technology to resource-scarce regions, addressing insufficient diagnostic capabilities.
· Drive Standardization: Establish unified quality control and data management processes to ensure consistency and reliability of cross-center diagnoses.
· Foster Technological Innovation: Leverage multicenter data accumulation to accelerate research in digital pathology and computational pathology, facilitating disciplinary breakthroughs.
Professor Wang emphasized that this initiative is not only a major breakthrough for Ruijin Hospital's Pathology Department but also a landmark exploration in the field of pathology. He called on more partners to join, leveraging technological sharing and collaboration to elevate global pathological diagnosis services and contribute to human health.
As a key ecosystem partner, WINMEDIC will continue to strongly support Ruijin Hospital's RuiPath Multicenter Plan and assist more institutions in participating. With its mature digital slide scanning systems, remote pathology consultation systems, digital slide management software, pathology teaching software, and full-process pathology management software, WINMEDIC will continuously iterate intelligent pathology department solutions, driving a qualitative leap in diagnostic efficiency and accuracy in the pathology industry.